REMFORM® II HS™
REMFORM® II HS™ is designed for direct assembly into high‑strength and fiber‑reinforced plastics. These screws feature the Unique Radius Flank™ asymmetrical thread form, which provides a larger contact surface with the thread flanks. This results in increased resistance to internal thread stripping and a more secure fastening. The optimized thread geometry also allows the screw to be reused with minimal risk of damage, further reducing the chance of stripping.
The graph below illustrates a comparison of threading curves for REMFORM® II HS™ and a standard screw for plastic, both diameter Ø6,0 mm in a PP + 20% glass fiber part, core hole Ø5,0 and 12 mm engagement length.
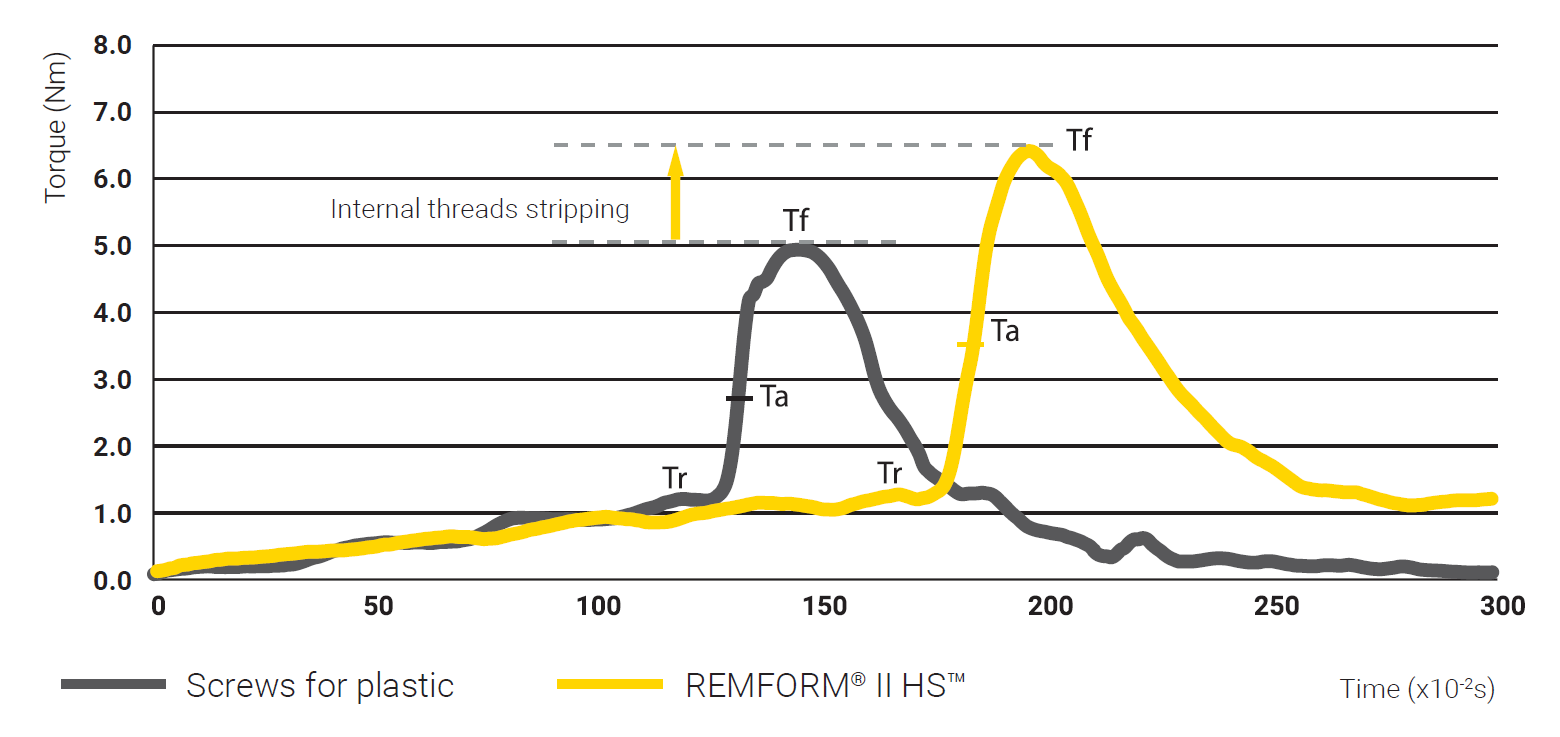
When comparing with a conventional screw for plastic, REMFORM® II HS™ screw offers greater safety during assembly (difference between threading torque and failure torque). The higher stripping torque guarantees a more reliable assembly process and an increased stability during installation.